This post explores the AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE), its specifications, performance in cryptocurrency mining, and overall efficiency. It provides a comparative analysis with modern GPUs and discusses its relevance in specific contexts.
The AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE), released in 2017, was designed as a high-end workstation graphics card, targeting professionals in data science, machine learning, and content creation. Its specifications reflect this ambition, featuring a powerful GPU with 4096 cores, a base clock of 1382 MHz, and a boost clock of 1600 MHz. The card is equipped with 16GB of High Bandwidth Memory 2 (HBM2), operating on a 2048-bit memory interface, providing a memory bandwidth of 483 GB/s. These specifications positioned the Vega FE as a capable solution for computationally intensive tasks.

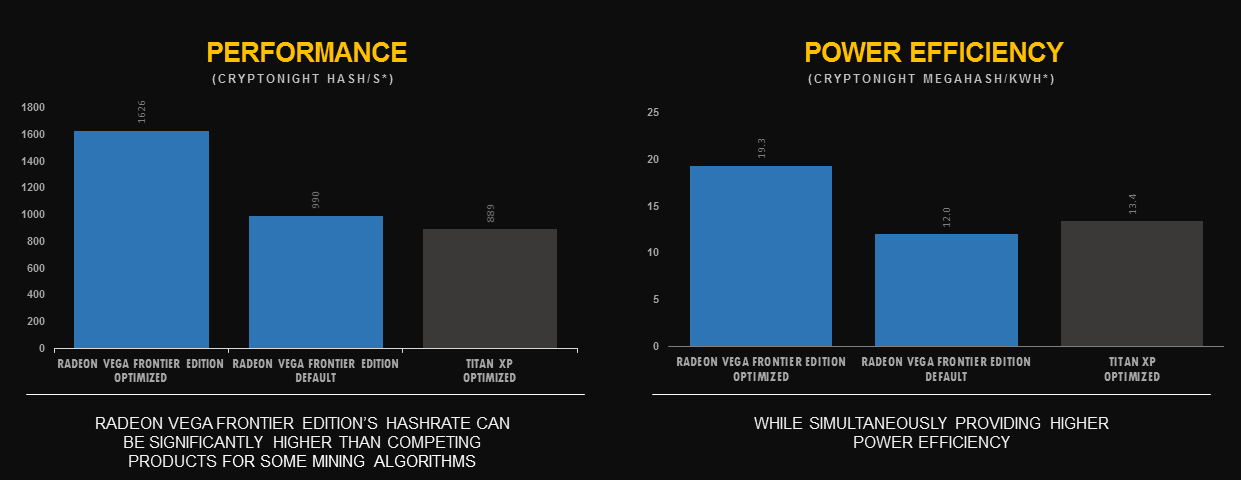
Mining Performance
During the cryptocurrency boom, the Vega FE was assessed for its mining capabilities. The card achieved a hash rate of approximately 32 MH/s for Ethereum mining at stock settings, which could be overclocked to around 37 MH/s. For Zcash mining, the Vega FE produced 440 sol/s, which increased to 489 sol/s with overclocking. Monero mining yielded 1850 H/s, which could be boosted to 2100 H/s through overclocking.
However, its power consumption was a significant drawback. The Vega FE consumed around 300 watts per hour, impacting its mining efficiency.
Overclocking Settings and Power Consumption
To optimize mining performance, users often applied specific overclocking settings. These included reducing the voltage by 20% and adjusting core and memory clocks. For Ethereum mining, a core clock of 1100 MHz and a memory clock of 1100 MHz were common. For Zcash and Monero, a core clock of 1500 MHz and a memory clock of 1100 MHz were used. Despite these optimizations, the Vega FE’s power consumption remained high at 300W per hour.
Mining Efficiency Analysis
The mining efficiency of the Vega FE can be evaluated by comparing its hash rate to its power consumption. For Ethereum, the Vega FE achieved approximately 0. 123 MH/s per watt (37 MH/s at 300W). This efficiency is considerably lower than that of modern GPUs. For instance, the RX 6600 XT achieves around 0. 27 MH/s per watt (32 MH/s at 120W), and the RTX 3060 achieves about 0. 29 MH/s per watt (50 MH/s at 170W). The Vega FE is approximately two to two and a half times less efficient than these newer cards.
Historical Context
The release of the Vega FE occurred during a period of intense interest in cryptocurrency mining. The demand for GPUs surged as individuals and organizations sought to capitalize on the profitability of mining various cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum, Zcash, and Monero. While the Vega FE was initially attractive due to its high computational capabilities, its high-power consumption and lower efficiency compared to newer GPUs eventually diminished its appeal for large-scale mining operations.
Impact and Influential Individuals
AMD’s Vega architecture was a significant development in GPU technology. It aimed to provide a versatile solution for both professional and gaming applications. Key individuals involved in the development and promotion of the Vega FE included AMD’s engineering teams and marketing personnel, who emphasized its capabilities for professional workloads and high-performance computing.
Various Perspectives
From a professional standpoint, the Vega FE was seen as a powerful tool for data analysis, machine learning, and content creation. Its high memory bandwidth and computational power made it suitable for tasks requiring substantial GPU resources. However, from a mining perspective, its high-power consumption and lower efficiency compared to newer GPUs made it less attractive for large-scale cryptocurrency mining operations.
Recent Developments and Future Potential
In recent years, the Vega FE has become less relevant for cryptocurrency mining due to the emergence of more efficient GPUs and ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) designed specifically for mining. However, it may still hold value for individuals with specific use cases, such as legacy rendering, old-school mining, or as a collector’s item for enthusiasts.
Relevance in Specific Contexts
The Vega FE may be a viable option under certain conditions:
Cheap Acquisition: If the card can be acquired for under $100–120, it may be cost-effective for specific tasks.
Low Electricity Costs: If electricity is free or very cheap, the high-power consumption is less of a concern.
Legacy Mining or Rendering: The Vega FE can be used for mining older cryptocurrencies or for legacy rendering tasks.
Enthusiast Collection: The card may appeal to collectors or enthusiasts interested in the history of GPU technology.
Advantages
High Computational Power: The Vega FE’s 4096 cores and high memory bandwidth make it capable for computationally intensive tasks.
Professional Applications: It is suitable for data analysis, machine learning, and content creation.
Disadvantages
High Power Consumption: The card consumes around 300W, making it less efficient compared to modern GPUs.
Lower Mining Efficiency: Its mining efficiency (MH/s per watt) is significantly lower than that of newer GPUs.
Limited Relevance: It is less relevant for modern cryptocurrency mining due to the availability of more efficient alternatives.
Overall Analysis
The AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE) was a powerful workstation graphics card that offered high computational capabilities. While it found some use in cryptocurrency mining, its high power consumption and lower efficiency compared to modern GPUs made it less attractive for large-scale mining operations. The Vega FE may still be viable for specific use cases, such as legacy rendering, old-school mining, or as a collector’s item.
Comparative Analysis with Modern GPUs
When comparing the Vega FE to modern GPUs, several key differences emerge, particularly in terms of efficiency and mining performance. Newer cards such as the RX 6600 XT and RTX 3060 offer significantly better hash rates per watt, making them more profitable for cryptocurrency mining. Additionally, modern GPUs often incorporate architectural improvements and power-saving technologies that enhance their overall performance and energy efficiency.
Specific Use Cases
Despite its limitations, the Vega FE may still be relevant in specific scenarios. For example, researchers or enthusiasts who require a GPU for legacy rendering tasks or for mining older cryptocurrencies may find the Vega FE to be a cost-effective option. Additionally, individuals with access to free or very cheap electricity may be less concerned about the card’s high-power consumption.
Future Developments
Looking ahead, the future of the Vega FE is limited due to the rapid advancements in GPU technology. Newer generations of GPUs offer significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and features, making the Vega FE increasingly obsolete for most applications. However, it may continue to hold niche value for specific use cases or as a collector’s item.
The AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE) was a significant development in GPU technology, offering high computational power and memory bandwidth. While it had some applications in cryptocurrency mining, its high-power consumption and lower efficiency compared to modern GPUs made it less attractive for large-scale mining operations. The Vega FE may still be viable for specific use cases, such as legacy rendering, old-school mining, or as a collector’s item, but its overall relevance is diminishing due to the emergence of more efficient and powerful GPUs. The Vega FE is approximately two to two and a half times less efficient than these newer cards. Its value today largely depends on its acquisition cost and the availability of cheap electricity, catering to niche applications or enthusiasts.
Summary of the AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE) Specifications :
- GPU Cores : 4096
- Base Clock : 1382 MHz
- Boost Clock : 1600 MHz
- Memory Interface : 2048-bit HBM2
- Memory Bandwidth : 483 GB/s
- Memory : 16GB
- Memory Clock : 1890 MHz

Ethereum Mining Hashrate : 32MH/s
OverClocking Hashrate : 37 MH/s
Zcash Mining Hashrate : 440 sol/s
OverClocking Hashrate : 489 sol/s
Monero Mining Hashrate : 1850 H/S
OverClocking Hashrate : 2100 sol/s
Summary of the AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE) Mining Hashrate :
- KECCAK Mining Hashrate : 754.20 MH/s
- DaggerHashimoto [ EtHash : (ETH) & (ETC) ] Mining Hashrate : 38.59 MH/s
- Decred (DCR) Mining Hashrate : 2.92 GH/s
- Cryptonight [ (XMR) & (XDN) ] Mining Hashrate : 1.2 kH/s
- Lbry ( LBC ) Mining Hashrate : 0.34 GH/s
- Equihash [ (ZEC – ZEN – ZCL) & (BTG) & (KMD) & (HUSH) ] Mining Hashrate : 494.08 Sol/s
- Pascal [ (PASC) & (PASL) ] Mining Hashrate : 1.76 GH/s
- X11GOST [ Sibcoin (SIB) ] Mining Hashrate : 14.50 GH/s
- SIACOIN (SC) Mining Hashrate : 2.36 GH/s
AMD Vega Frontier Edition (FE) OverClocking Settings :
- Voltage : -20%
- Core :
- Ethereum : 1100
- Zcash : 1500
- Monero : 1500
- Memory : 1100
Power Consumption : 300 Watt/Per Hour.




