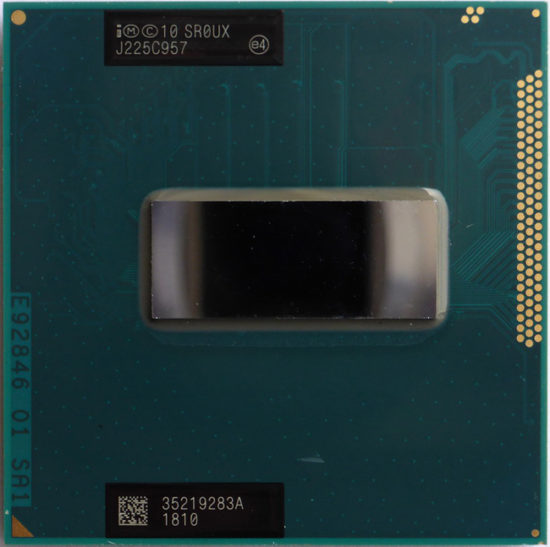
The Intel Core i7-3630QM, launched in 2012, represents a significant achievement in mobile CPU technology. As part of Intel’s third generation of Core processors, codenamed Ivy Bridge, this processor was engineered for high-performance laptops designed for tasks demanding substantial computational power. This post will look into its specifications, performance capabilities, historical significance, and the context of its application, particularly in the realm of cryptocurrency mining, which has become a focal point in the recent technological landscape.

Specifications and Features
The Intel Core i7-3630QM boasts impressive specifications that marked a notable improvement over its predecessors. With a base frequency of 2. 40 GHz and a maximum turbo frequency of 3. 40 GHz, the i7-3630QM was designed to handle demanding applications efficiently. It features four cores and supports eight threads, positioning it well for multitasking environments. The processor carries a cache size of 6 MB SmartCache and operates with a bus speed of 5 GT/s DMI3, allowing for swift data transactions.
Moreover, one of its remarkable advancements is the 22nm fabrication process. This smaller fabrication size not only enhances performance per watt but also improves energy efficiency in comparison to the 32nm process used in the previous Sandy Bridge architecture. Additionally, the i7-3630QM integrates Intel HD Graphics 4000, which delivers decent graphical performance for casual gaming and multimedia consumption.
Historical Significance and Technological Impact
When examining the historical significance of the i7-3630QM, it is essential to recognize the competitive landscape of mobile processors during the early 2010s. Intel’s decision to adopt the Ivy Bridge architecture was partly in response to AMD’s increasing market pressure, as AMD was also innovation-focused with its A-Series APUs. The i7-3630QM, therefore, was not just a product of technological advancement but also a strategic response to evolving market demands for more powerful yet energy-efficient mobile solutions.
The contributions of key individuals at Intel, particularly those involved in the development of the Ivy Bridge architecture, cannot be overlooked. The work of engineers and researchers who pushed the boundaries of chip design enabled Intel to maintain its market leadership. The emphasis on both enhanced performance and energy efficiency paved the way for burgeoning fields such as mobile computing, where users demand high performance without compromising battery life.
Use Cases and Performance
Although primarily aimed at high-end laptops, the i7-3630QM has found applications across various fields including gaming, graphic design, and engineering tasks. Users benefit from its ability to handle memory-intensive applications and tasks that require significant processing power, such as video editing and 3D rendering. This processor’s performance capability is evident in multi-threaded applications, where the support for eight threads allows for efficient execution of tasks processing large datasets or performing complex calculations.
However, a fascinating area of discussion regarding the i7-3630QM is its performance in cryptocurrency mining. As the popularity of crypto mining surged, enthusiasts tested various hardware to optimize their mining rigs. While the i7-3630QM is not specifically designed for mining, its specifications allow for limited functionality in that domain. The mining hash rates for various algorithms demonstrate this: 0. 55 MH/s for LYRA2RE, 0. 28 kH/s for HODL, and a modest 14. 25 Sol/s for Equihash-based cryptocurrencies. While these figures are noteworthy, they fall significantly short of modern dedicated ASIC miners and even more recent GPU setups.
Cryptocurrency Mining: A Misfit for i7-3630QM
As the cryptocurrency landscape has evolved, so too have the demands on hardware. The energy efficiency necessary for profitable mining has become the prevailing standard, and unfortunately, the i7-3630QM does not meet these requirements. With a power consumption of 45 Watts per hour, its energy costs can quickly accumulate. For instance, a monthly power use calculation indicates a consumption of 32. 4 kWh, leading to an estimated electricity cost of R90. 72 per month, or approximately $4. 80 at pricing applicable in certain regions.
While an estimated mining yield of around $0. 08 to $0. 15 per month exists when using the i7-3630QM under optimal conditions, the arithmetic is far from favorable for miners. With expenses surpassing potential earnings, it becomes evident that utilizing this processor for mining results in a net loss, making it impractical as a mining rig.
Analyzing Future Developments
Looking ahead, the relevance of the Intel i7-3630QM serves as a case study for understanding how technology evolves to meet advancing needs. As new generations of processors emerge, incorporating features like improved machine learning capabilities, and dedicated graphics architecture, older models like the i7-3630QM inevitably fall behind. While it may still hold some value for basic computing tasks today, it stands as a reminder of how rapidly technology can change.
In the context of cryptocurrency mining, where hardware requirements continuously shift to embrace higher efficiency and performance, it is apparent that older processors are likely to become obsolete. The advancements in ASIC technology and specialized GPUs indicate that CPU mining will not only be unprofitable but increasingly impractical for competitive participants.
In summary, the Intel Core i7-3630QM processor marked a pivotal moment in mobile computing when it launched in 2012. Its robust specifications, combined with innovations in efficiency and performance, offered a powerful solution for users at the time. Although it remains a valuable option for basic computing tasks today, its application in cryptocurrency mining illustrates the prevailing challenges faced by aging technology amid an ever-evolving landscape.
Summary of the Intel Core i7-3630QM Processor Specifications :
- Processor Base Frequency : 2.40 GHz
- Max Turbo Frequency : 3.40 GHz
- Cores : 4
- Threads : 8
- Cache : 6 MB SmartCache
- Bus Speed : 5 GT/s DMI3

Summary of the Intel Core i7-6700 Processor Mining Hashrate :
- LYRA2RE Mining Hashrate : 0.55 MH/s
- HODL Mining Hashrate : 0.28 kH/s
- Cryptonight [ (XMR) & (XDN) ] Mining Hashrate : 0.1 kH/s
- Equihash [ (ZEC – ZEN – ZCL) & (BTG) & (KMD) & (HUSH) ] Mining Hashrate : 14.25 Sol/s
Power Consumption : 45 Watts/Per Hour.